Available methods¶
There are three built-in methods in ORIGAMI-MS, namely linear, boltzmann and exponential which have been designed
around improving the quality of CIU/aIMS acquired data. The final method, user-defined allows usage of arbirary
lists of scans per voltage and collision voltages, giving you all the freedom you should need.
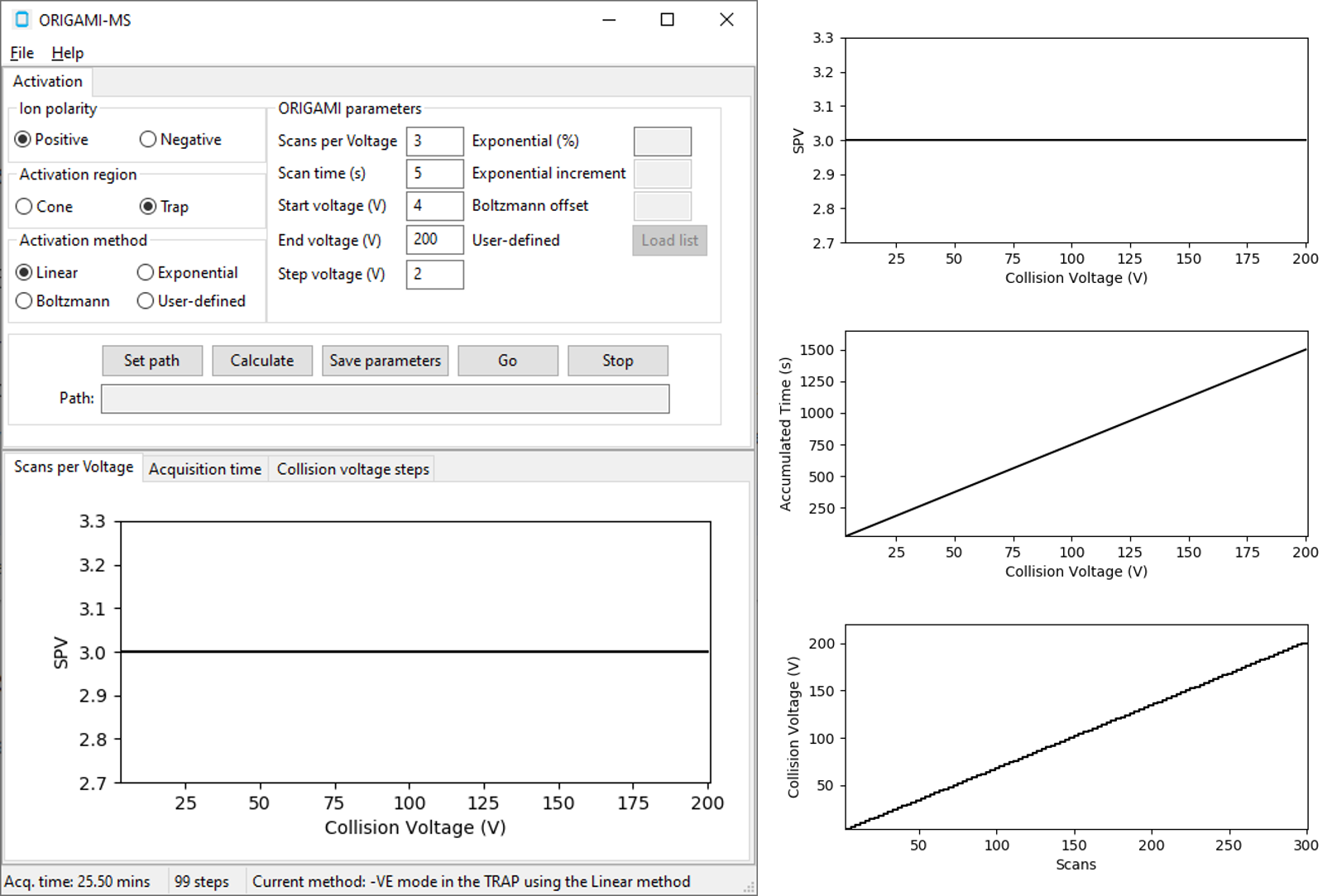
Linear¶
The linear method follows simple priciple of having the same number of scans for each collision voltage increment.
This makes the acquisition and analysis very straightforward, however, can have detrimental effect on the overall quality
of the data when signal-to-noise ratios go down.
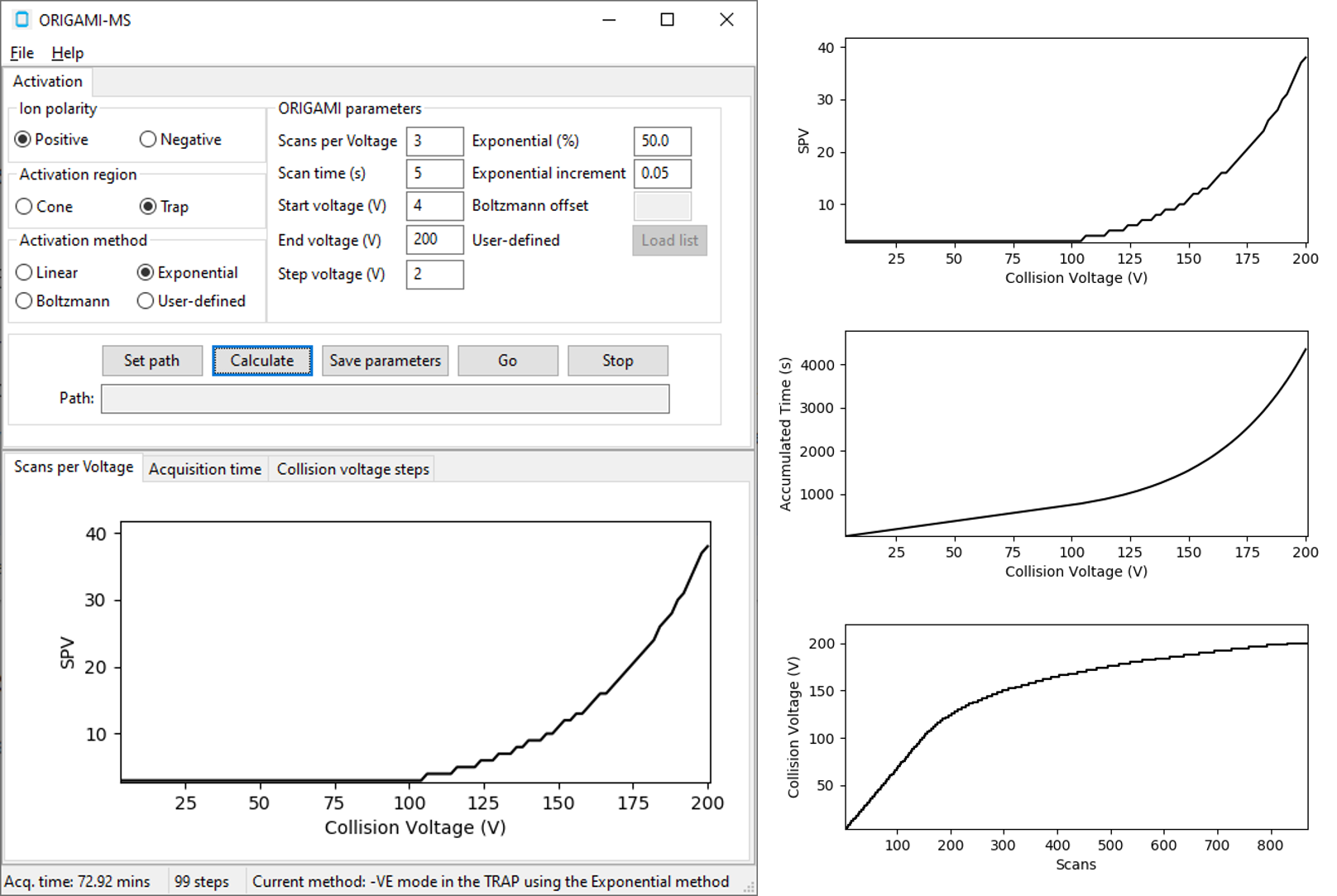
Exponential¶
The exponential method uses an exponential model to systematically increase the number of scans as the collision voltage
increases, which can improve data quality. This of course, will lead to longer acquisition times.
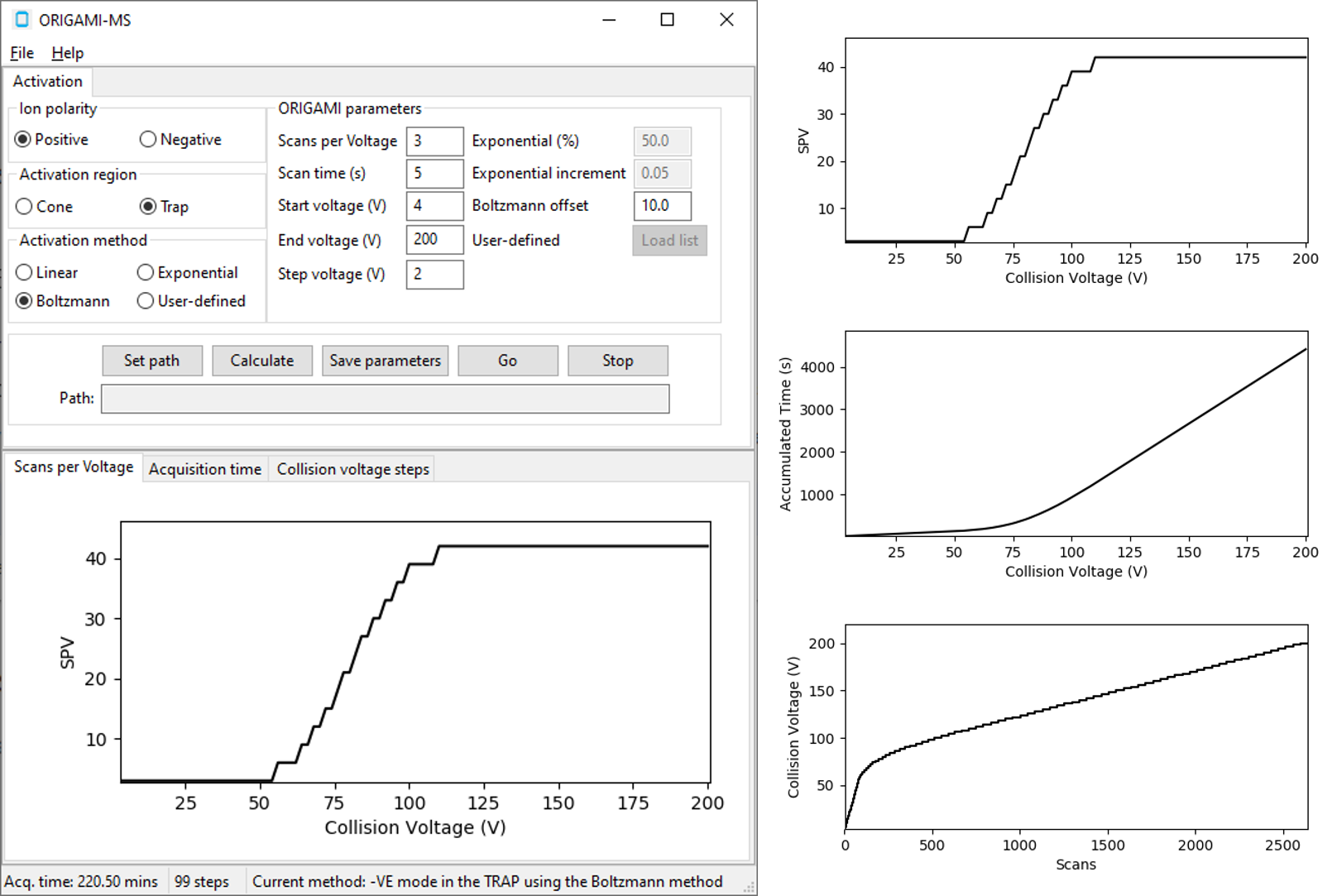
Boltzmann¶
The boltzmann method uses a Boltzmann equation to model systematically increase the number of scans as the collision voltage
increases, which can improve data quality. This of course, will lead to longer acquisition times.
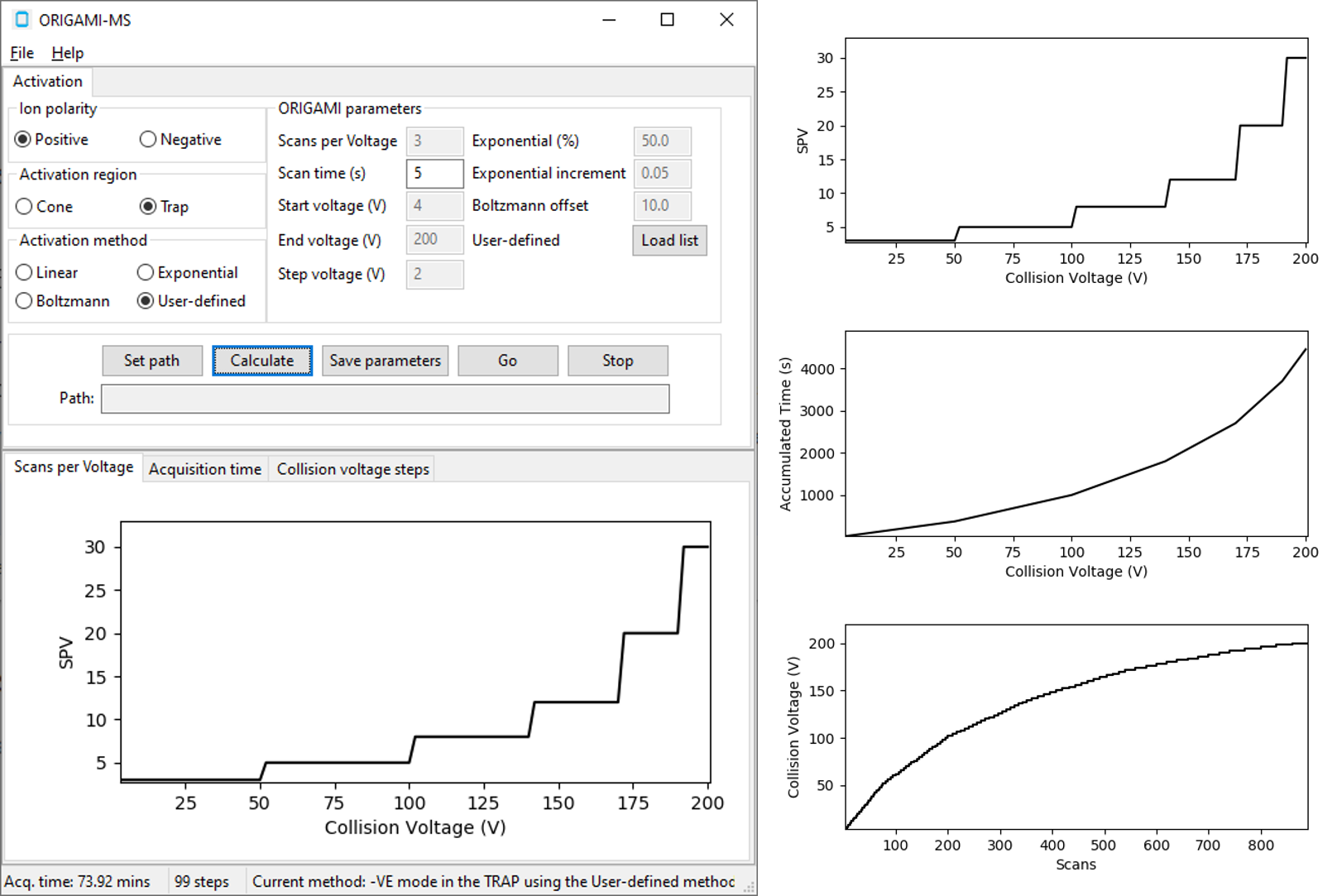
User-defined¶
As the suggests, you define your own parameters which will be used during the data acquisition. See example file for inspiration in what should be included in the CSV file.